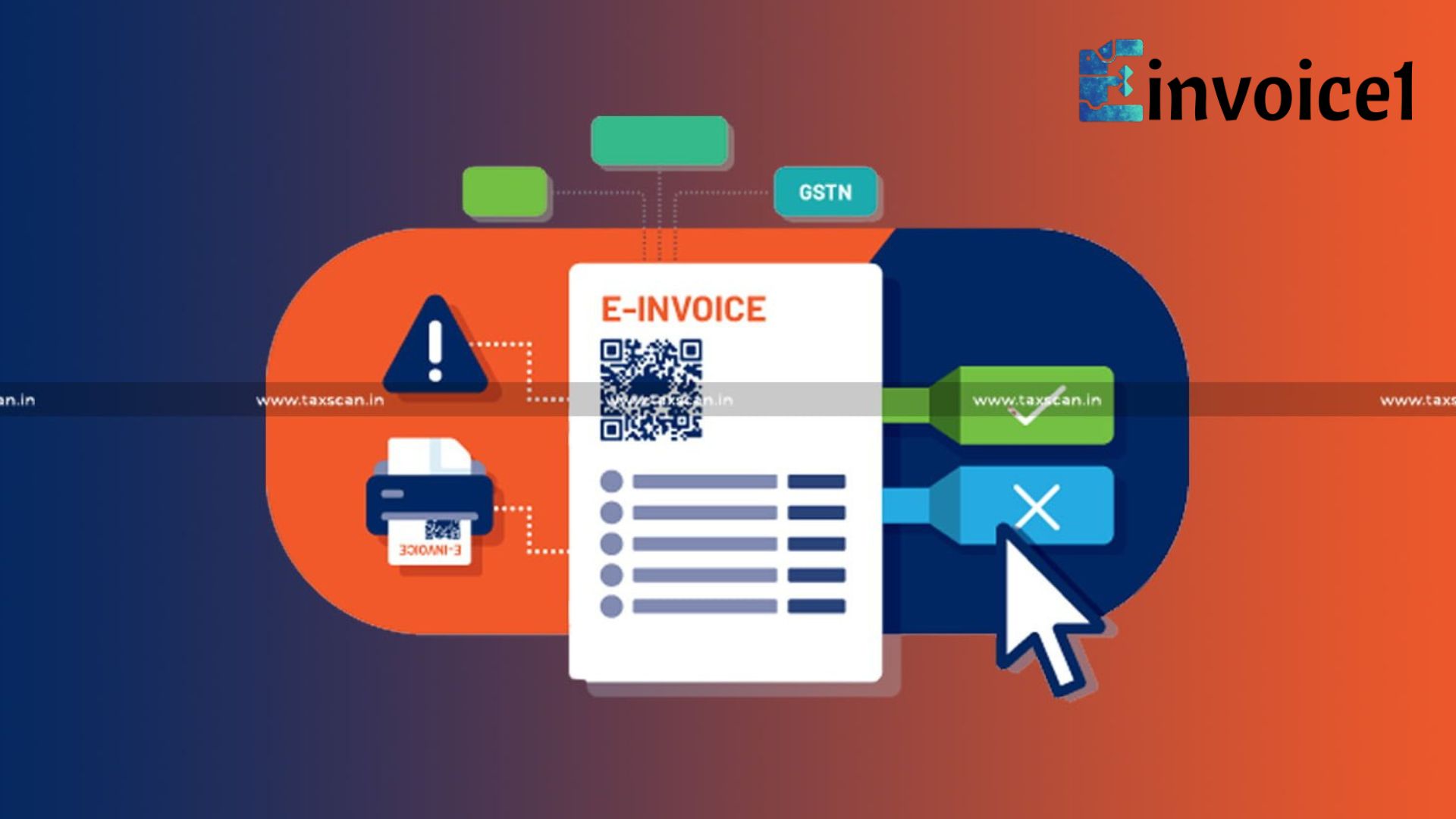
Electronic invoicing, often called E Invoice, is becoming one of the most important tools for modern businesses. In a digital economy where speed, accuracy, and compliance are crucial, E Invoice offers a reliable way for companies to manage their billing and reporting. Instead of relying on traditional paper invoices or scattered spreadsheets, organizations can now generate, share, and archive invoices digitally, saving time while reducing human errors. Governments across the globe are also recognizing the efficiency of E Invoice systems and are gradually mandating their use. This transformation is not only about digitization, but also about transparency, sustainability, and the evolution of business processes.
The concept of E Invoice is simple yet powerful. It replaces physical paper by utilizing electronic formats that can be more readily tracked, secured and integrated into accounting systems. At the heart of it, it makes invoices between suppliers and buyers standardized and machine-readable, meaning fewer disputes and quicker settlements. Beyond efficiency, E Invoice also ensures regulatory compliance since the data can be directly shared with tax authorities in real time. This reduces fraud, prevents tax evasion and helps to build trust in financial reporting. The advantages for businesses are huge and far-reaching beyond the reduced costs.
The importance of E Invoice1 has grown significantly as international trade has become more connected. For large organizations with operations across multiple countries, the need to adhere to compliance standards in each country can be challenging to manage invoicing requirements. E Invoice platforms solve this challenge by offering standardization across borders. Whether working with customers in Europe, Asia, or North America, adhering to established international standards ensures that companies have a consistent process for managing their invoicing. This also means faster penetration of new markets as businesses no longer have to reinvent their reporting process for every individual market.
One of the biggest advantages of E Invoice1 is the speed with which transactions can be processed. Historically, business delays were common, caused by mail delays, manual data collection and entry, and slow approvals. These delays have created cash flow problems, disputes, and inefficiencies throughout supply chains. With E Invoice, the entire process is streamlined. Once a service is delivered or goods are shipped, the invoice can be automatically generated and sent to the customer. It gets to the customer immediately, after which it verifies its correctness and the customer can authorize payment. Additionally, this automated flow cuts down time from days or even weeks in the payment cycle, allowing for businesses to have more robust liquidity and improved financial planning.
Another critical aspect of E Invoice is its role in sustainability. Paper invoicing is expensive because it is time consuming and also not good for the environment. Not only do millions of trees get cut down every year for the production of paper, but conventional invoicing also needs to be stored, printed, and shipped. By shifting to E Invoice, companies contribute to reducing carbon emissions and waste. Many corporations use electronic invoicing as part of their corporate social responsibility efforts, demonstrating their dedication to a more environmentally conscious form of business. For modern consumers that are concerned about sustainability, it can also be a positive branding activity that can add value to the reputation of the business.
Small and medium-sized enterprises, often referred to as SMEs, also benefit significantly from E Invoice adoption. While large organizations have advanced accounting departments and IT infrastructure, smaller businesses may have to make do with more limited resources. Implementing E Invoice allows SMEs to compete on a more level playing field by reducing administrative burdens. Instead of hiring extra staff to manage paperwork, a small business can use an automated platform that generates accurate invoices, tracks payments, and even integrates with their tax filing requirements. This efficiency frees up business owners to concentrate more on expansion and less on mundane administrative duties.
Government regulations are a major driver of E Invoice1 adoption. In countries like India, Mexico, Brazil, and Italy, E Invoice has become mandatory for certain categories of businesses. The main reason is to fight tax evasion and provide a proper reflection of financial transactions. For instance, in India, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework requires specific businesses to generate invoices in electronic format so that data flows directly to the government’s GST system. This real-time data sharing promotes transparency and minimizes the risk of error. It is likely that such policies will be extended into more countries as the advantages of standardised invoicing become more widely understood over the next few years.
The integration of E Invoice into enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems is another major milestone in digital transformation. Modern ERP systems allow invoicing to be automatically created when a purchase order has been delivered. This interval and data automation eliminates the need for data to be entered twice and provides a smaller margin of error in the event of data mismatches. Additionally, real-time reporting gives companies the accuracy to track revenue and expenses. In businesses that are dependent on a complex supply chain such as manufacturing and retail, this seamless integration translates into efficiency across multiple departments. Finance teams, procurement, and compliance officers all can use the same data, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Security is an important consideration in the adoption of E Invoice1. While some may worry about cyber risks, in reality, E Invoice systems are often more secure than traditional methods. Paper invoices can be lost, forged or tampered with, while electronic invoices can be encrypted, tracked and verified with digital signatures. Many platforms also have audit trails to identify when an invoice was created, sent, or modified as well as who made the changes. This transparency helps to minimize potential fraud and create more accountability within organizations. By combining secure technology with regulatory oversight, E Invoice systems provide a trustworthy framework for financial transactions.
Cross-border trade is another area where E Invoice is playing a transformative role. Global supply chains contain multiple currencies, multiple languages, and multiple tax systems. Traditional invoicing was often delayed by conversion errors, language discrepancies and compliance loopholes. E Invoice platforms with multilingual and multi-currency support remove these barriers by automatically adjusting invoices to meet the standards of each region. This makes international operations easier and less likely to cause disputes among trading partners. For exporters and importers alike, it means faster payments; cost savings in compliance; and increased confidence with overseas clients.
One of the challenges businesses face in adopting E Invoice1 is the initial transition. Moving from paper-based systems to digital systems takes training, investment, and change management. Employees might need to learn new software and existing processes may need to change. However, once the system is up and running, the long-term advantages will certainly outweigh the short-term difficulties. Many companies are reporting large cost savings after the first year of implementation. They also point out increased satisfaction from both employees and customers because of speedier processing and fewer disputes.
The future of E Invoice1 looks promising as more countries adopt mandatory frameworks and technology continues to evolve. Blockchain technology, for instance, has the potential to enhance E Invoice systems even further by providing immutable records of transactions. This would help increase trust between businesses and regulators while further decreasing fraud. As global commerce continues to expand, the demand for secure, fast, and standardized invoicing will only grow, making E Invoice a central feature of digital economies worldwide.